Using Incorta and PySpark Linear Regression ML package to predict eCommerce Customer
Project Overview
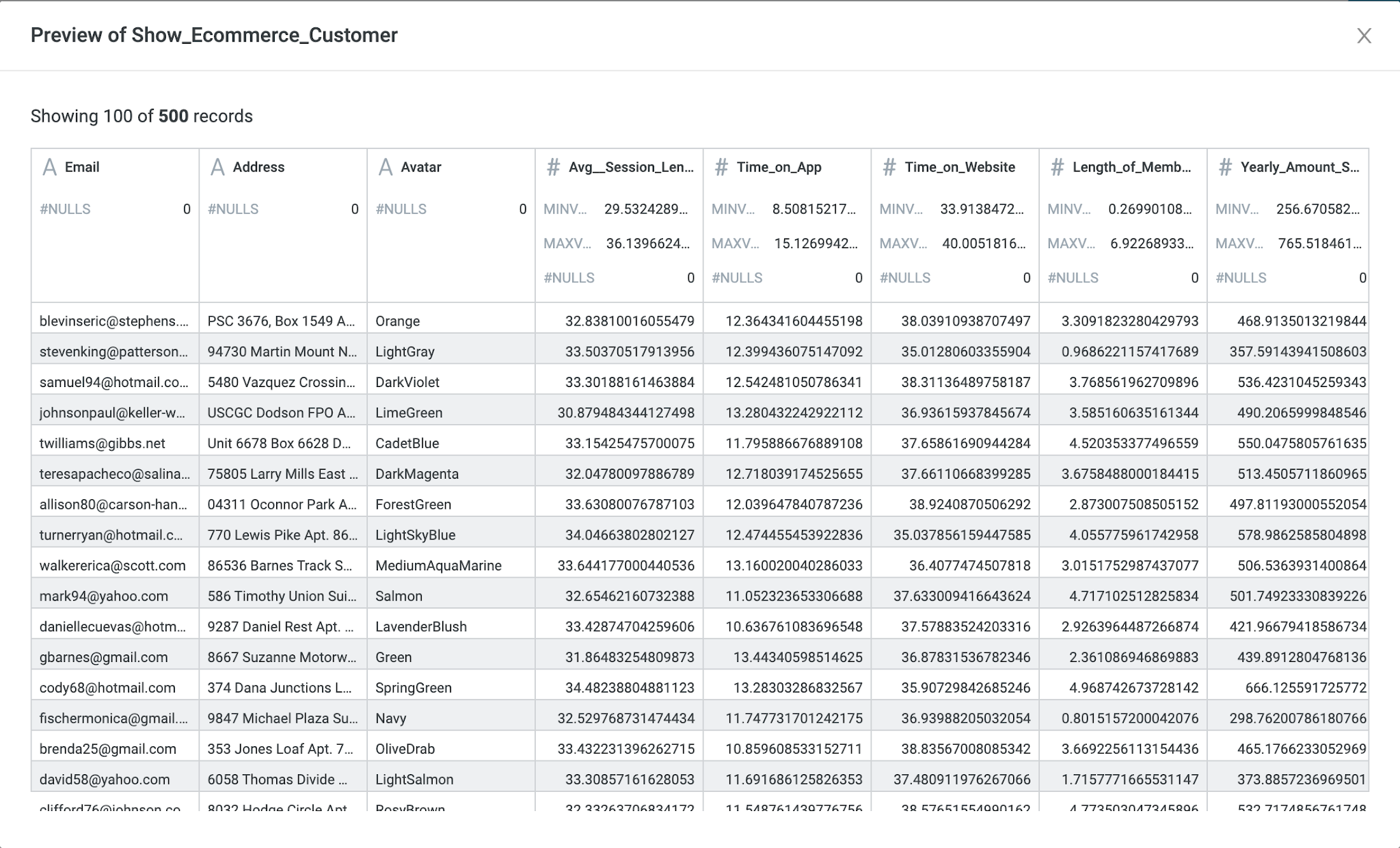
I got a dataset from kaggle.com.
Assumption: eCommerce company based in New York City that sells clothing online but they also have in-store style and clothing advice sessions. Customers come into the store, have sessions or meetings with a personal stylist, then they can go home and order either on a mobile app or website for the clothes they want.
We need to predict 'Yearly Amount Spent'
Here are the features or attributes collected in the dataset:
- 'Avg__Session_Length'
- 'Time_on_App'
- 'Time_on_Website'
- 'Length_of_Membership'
Step 1: Upload csv file in incorta.
Upload the CSV file to Incorta, and add a file table in the schema named Ecommerce_Customer.
Step 2: Read the Ecommerce Customer file
Use PySpark to read the table named SparkTesting.Ecommerce_Customer.
The CSV file loaded into Incota can be read into PySpark using
Step 3: VectorAssemblerTest
Use VectorAssembler combine 'Avg__Session_Length', 'Time_on_App', 'Time_on_Website' and 'Length_of_Membership' into a single feature vector called 'features'.
Step 4: Split data into Training and Testing data sets
The PySpark randomSplit function randomly samples the data to help ensure that the testing and training sets are similar. I split the data into two sets, 70% used in training, and 30% used in testing.Step 5: Train data
I use PySpark LinearRegression to train a linear regression model and extract model summary statistics.
Step 6: Test model
For evaluating the linear regression model, I used 30% of data as testing data and used RMSE and R2 to evaluate the model.
Step 7: Prediction
The final product is the model that we can use for predicting 'Yearly_Amount_Spent' for unlabeled data.











Thank you for sharing the post keep posting growth partner ecommerce if you looking to start your own ecommerce business.
ReplyDelete